
Introduction
Welding is the process of joining metals, is universal used in various industries. At APAC, we use soldering for the majority of our edge protection systems when producing.
There are three important welding methods: TIG welding, MIG welding, and laser welding in our factory. Each method has its own unique characteristics and applications, and understanding the differences between these welding methods is critical. Let's learn more about them.
TIG Welding
Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) welding, also known as Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW), is a type of welding process that uses a tungsten electrode to produce the weld, is a precise and versatile welding method widely used in various industries.
TIG welding's principle is that two metal parts use an electric arc that is created between a non-consumable tungsten electrode and the base metal. that provides the current and heat to the metal parts, The tungsten electrode is held in a TIG torch, As the tungsten electrode heats up, it creates a small pool of molten metal on the surface of the base metal. The welder then adds a filler metal into the molten pool to join the two metal parts together. The arc and the shielding gas are carefully controlled by the welder to create a precise and clean weld.

Advantages of TIG Welding
- Precision: TIG welding provides a high degree of precision and control over the welding process, allowing for clean, precise welds with minimal distortion or warping.
- Aesthetics: TIG welding produces clean, smooth welds that are visually appealing and require minimal post-welding finishing.
- Versatility: TIG welding can be used on a variety of metals, including aluminum, stainless steel, copper, brass, and titanium.
- Minimal spatter: Compared to other welding processes, TIG welding produces minimal spatter, reducing the need for costly and time-consuming cleaning and finishing after welding.
- Versatility: TIG welding can be used on a variety of metals, including aluminum, stainless steel, copper, brass, and titanium.
Disadvantages of TIG Welding
- Complexity: TIG welding requires a high level of skill and experience to produce high-quality welds consistently, making it more challenging to learn and master. It also involves more equipment than other welding processes, making it more expensive and complex.
- Slow speed: TIG welding is a relatively slow process, making it less suitable for high-production welding applications.
- Tungsten electrode maintenance: The tungsten electrode used in TIG welding can be easily contaminated or damaged, leading to poor weld quality and requiring frequent replacement.
- Cost: TIG welding equipment is generally more expensive than equipment used for other welding processes, making it less accessible to some welders.
Application of TIG Welding
TIG welding finds applications in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, nuclear, and precision fabrication. It is commonly used for welding thin materials, intricate joints, and critical components that require high-quality welds. TIG welding is also favored for its ability to weld dissimilar metals. In construction, MIG Welding usually used in weld aluminum.
MIG Welding
MIG welding, also known as Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW), is a popular technique. The principle behind MIG welding involves feeding a continuous wire electrode through a welding gun connected to a power source. The arc is created when the wire comes into contact with the workpiece, generating intense heat that melts the electrode wire and fuses it with the base metal to form a solid and strong weld joint.
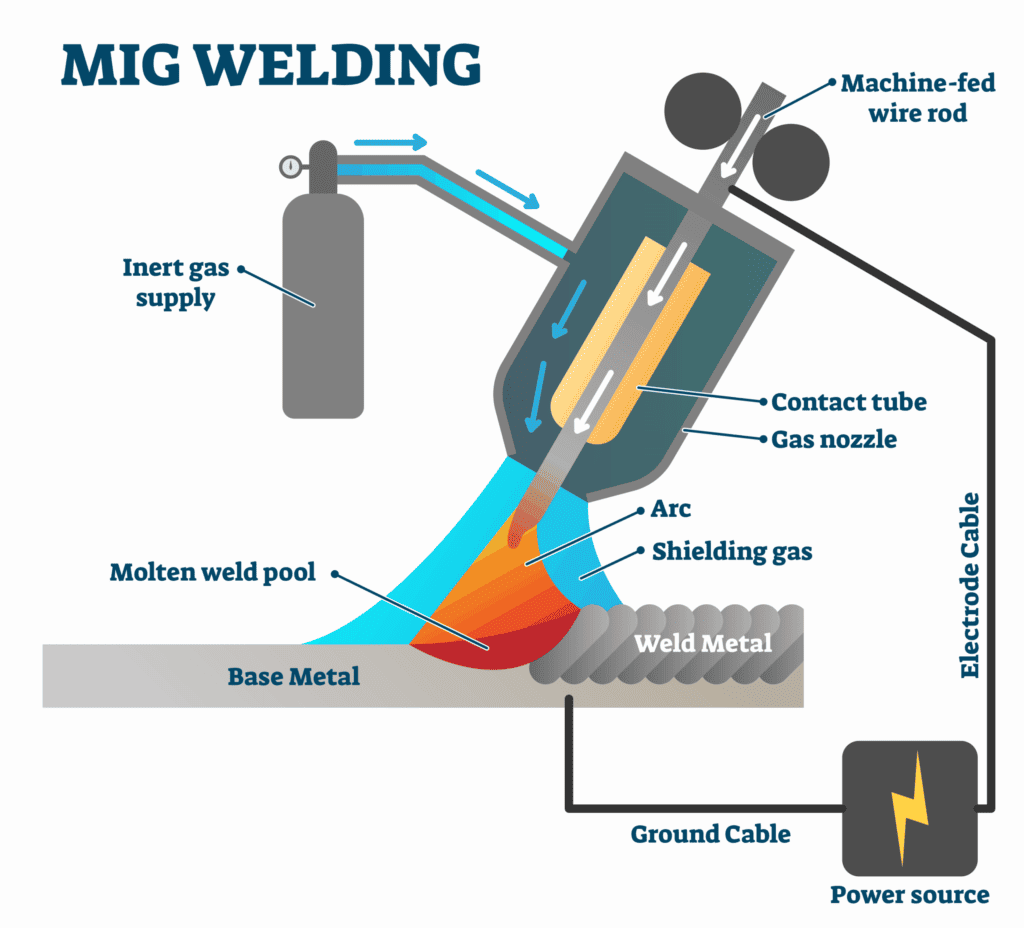
Advantages and disadvantages of MIG Welding
MIG welding offers several advantages. It is known for its high productivity due to the continuous wire feed, enabling rapid welding speeds. Additionally, it is relatively easy to learn and operate, making it suitable for beginners. MIG welding also provides excellent control over the weld bead, allowing for precise and consistent welds.
However, MIG welding does have some drawbacks. It can be more sensitive to wind and drafts than other welding methods due to the reliance on the gas shield. Additionally, MIG welding produces more spatter than techniques like TIG welding. Furthermore, the initial setup cost can be higher due to the need for a shielding gas supply and a wire feeder.
Applications of MIG Welding
MIG welding remains a versatile and widely used welding method in various industries. All thanks to its speed, ease of use, and ability to handle different materials.
MIG welding is commonly used in the construction industry to weld structural steel and fabrication work.
Laser Welding
Laser welding is a welding process that uses a high-powered laser beam to create a fusion between two metal parts.
The laser beam, which is highly focused and directed by optics, produces an intense heat source that melts the metal being welded. As the metal cools and solidifies, a strong and precise weld is formed.

Advantages and disadvantages of Laser Welding
The advantages of laser welding are numerous. It offers exceptional accuracy, producing narrow and deep welds with minimal distortion. The highly controllable process allows for precise heat input and minimal thermal impact on surrounding areas. Laser welding is also known for its speed and efficiency, enabling rapid production rates.
However, laser welding does have some drawbacks. The equipment and setup costs can be significant, making it less accessible for small-scale operations. Additionally, the process is highly sensitive to surface conditions and requires skilled operators for optimal results.
Applications of Laser Welding
Laser welding finds applications in various industries. It is commonly used in the automotive sector for joining body components and engine parts. It is also used in aerospace to weld thin and delicate components.
In construction, laser welding is usually used to weld steel fences.
Furthermore, laser welding is utilized in electronics manufacturing, medical device fabrication, and jewelry production.


